DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORK
![]()
Development Methodology:
SN | Framework Activities | Action |
1. | Discovery, Planning & Design |
|
2. | Development & Testing |
|
3. | Implementation & User Training |
|
API Integration Methodology:
SN | Framework Activities | Action |
1. | Discovery, Planning & Design |
|
2. | Development & Testing |
|
3. | Implementation & User Training |
|
IoT Integration Methodology:
SN | Framework Activities | Action |
1. | Discovery, Planning & Design |
|
2. | Development & Testing |
|
3. | Implementation & User Training |
|
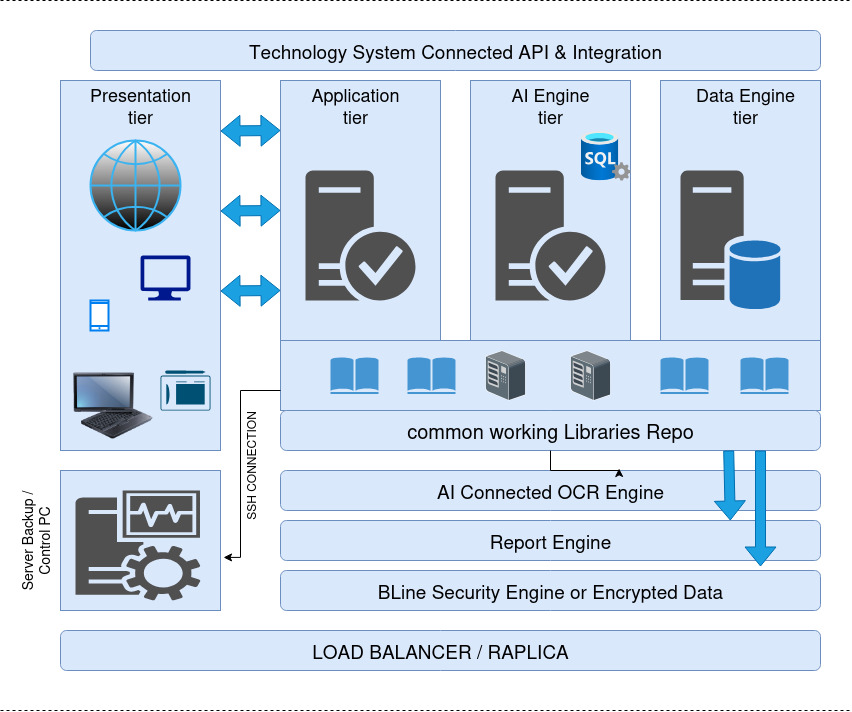
Platform Architecture